TLA stands for Three Letter Acronym. The world is full of TLAs. The IT world is indeed full of TLAs. The Data Management world is also full of TLAs. Here are 10 TLAs from the data management space that surrounds Master Data Management:
MDM: Master Data Management can be defined as a comprehensive method of enabling an enterprise to link all of its critical data to a common point of reference. When properly done, MDM improves data quality, while streamlining data sharing across personnel and departments. In addition, MDM can facilitate computing in multiple system architectures, platforms and applications. You can find the source of this definition and 3 other – somewhat similar – definitions in the post 4 MDM Definitions: Which One is the Best?
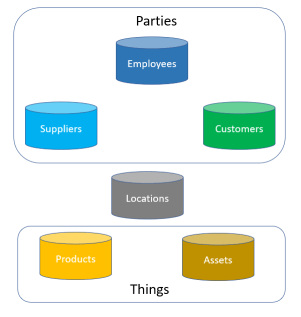
The most addressed master data domains are parties encompassing customer, supplier and employee roles, things as products and assets as well as location.
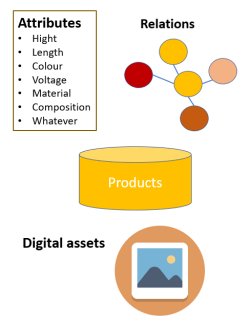
PIM: Product Information Management is a discipline that overlaps MDM. In PIM you focus on product master data and a long tail of specific product information – often called attributes – that is needed for a given classification of products.
Furthermore, PIM deals with how products are related as for example accessories, replacements and spare parts as well as the cross-sell and up-sell opportunities there are between products.
PIM also handles how products have digital assets attached.
This data is used in omni-channel scenarios to ensure that the products you sell are presented with consistent, complete and accurate data. Learn more in the post Five Product Information Management Core Aspects.

DAM: Digital Asset Management is about handling extended features of digital assets often related to master data and especially product information. The digital assets can be photos of people and places, product images, line drawings, certificates, brochures, videos and much more.
Within DAM you are able to apply tags to digital assets, you can convert between the various file formats and you can keep track of the different format variants – like sizes – of a digital asset.
You can learn more about how these first 3 mentioned TLAs are connected in the post How MDM, PIM and DAM Stick Together.
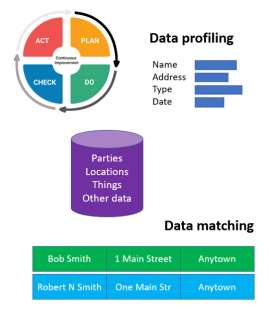
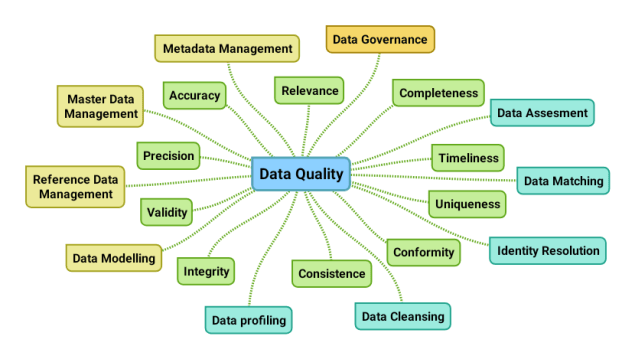
DQM: Data Quality Management is dealing with assessing and improving the quality of data in order to make your business more competitive. It is about making data fit for the intended (multiple) purpose(s) of use which most often is best to achieved by real-world alignment. It is about people, processes and technology. When it comes to technology there are different implementations as told in the post DQM Tools In and Around MDM Tools.
The most used technologies in data quality management are data profiling, that measures what the data stored looks like, and data matching, that links data records that do not have the same values, but describes the same real world entity.
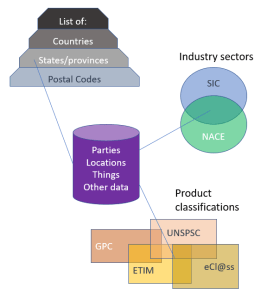
RDM: Reference Data Management encompass those typically smaller lists of data records that are referenced by master data and transaction data. These lists do not change often. They tend to be externally defined but can also be internally defined within each organization.
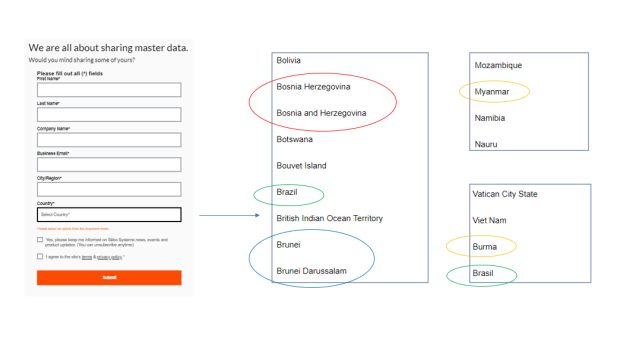
Examples of reference data are hierarchies of location references as countries, states/provinces and postal codes, different industry code systems and how they map and the many product classification systems to choose from.
Learn more in the post What is Reference Data Management (RDM)?

CDI: Customer Data Integration is considered as the predecessor to MDM, as the first MDMish solutions focused on federating customer master data handled in multiple applications across the IT landscape within an enterprise.
The most addressed sources with customer master data are CRM applications and ERP applications, however most enterprises have several of other applications where customer master data are captured.
You may ask: What Happened to CDI?
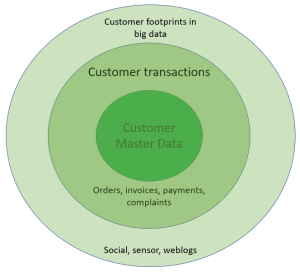
CDP: Customer Data Platform is an emerging kind of solution that provides a centralized registry of all data related to parties regarded as (prospective) customers at an enterprise.
In that way CDP goes far beyond customer master data by encompassing traditional transaction data related to customers and the emerging big data sources too.
Right now, we see such solutions coming both from MDM solution vendors and CRM vendors as reported in the post CDP: Is that part of CRM or MDM?
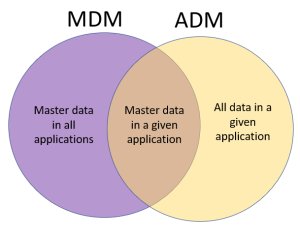
ADM: Application Data Management is about not just master data, but all critical data that is somehow shared between personel and departments. In that sense MDM covers all master within an organization and ADM covers all (critical) data in a given application and the intersection is looking at master data in a given application.
ADM is an emerging term and we still do not have a well-defined market – if there ever will be one – as examined in the post Who are the ADM Solution Providers?
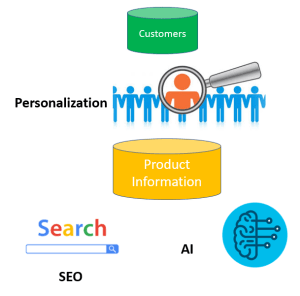
PXM: Product eXperience Management is another emerging term that describes a trend to distance some PIM solutions from the MDM flavour and more towards digital experience / customer experience themes.
In PXM the focus is on personalization of product information, Search Engine Optimization and exploiting Artificial Intelligence (AI) in those quests.
Read more about it in the post What is PxM?
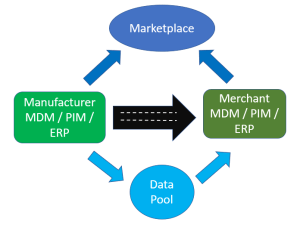
PDS: Product Data Syndication connects MDM, PIM (and other) solutions at each trading partner with each other within business ecosystems. As this is an area where we can expect future growth along with the digital transformation theme, you can get the details in the post What is Product Data Syndication (PDS)?
One example of a PDS service is the Product Data Lake solution I have been working with during the last couple of year. Learn why this PDS service is needed here.