The term Application Data Management (ADM) has recently been circulating in the Master Data Management (MDM) world as touched in The Disruptive MDM List blog post MDM Fact or Fiction: Who Knows?
Not at least Gartner, the analyst firm, has touted this as one of two Disruptive Forces in MDM Land. However, Gartner is not always your friend when it comes to short, crisp and easy digestible definitions and explanations of the terms they promote.
In my mind the two terms MDM and ADM relates as seen below:

So, ADM takes care of a lot of data that we do not usually consider being master data within a given application while MDM takes care of master data across multiple applications.
The big question is how we handle the intersection (and sum of intersections in the IT landscape) when it comes to applying technology.
If you have an IT landscape with a dominant application like for example SAP ECC you are tempted to handle the master data within that application as your master data hub or using a vendor provided tightly integrated tool as for example SAP MDG. For specific master data domains, you might for example regard your CRM application as your customer master data hub. Here MDM and ADM melts into one process and technology platform.
If you have an IT landscape with multiple applications, you should consider implementing a specific MDM platform that receives master data from and provides master data to applications that takes care of all the other data used for specific business objectives. Here MDM and ADM will be in separated processes using best-of-breed technology.
 While every data quality dimension applies to all domains of Master Data Management (MDM), some different dimensions apply a bit more to one of the domains or the intersections of the domains as explained in the post
While every data quality dimension applies to all domains of Master Data Management (MDM), some different dimensions apply a bit more to one of the domains or the intersections of the domains as explained in the post 





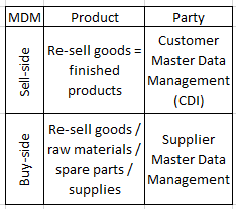 The core party and product picture could look like examined in the post
The core party and product picture could look like examined in the post 